Basic First Aid Skills for Preparedness
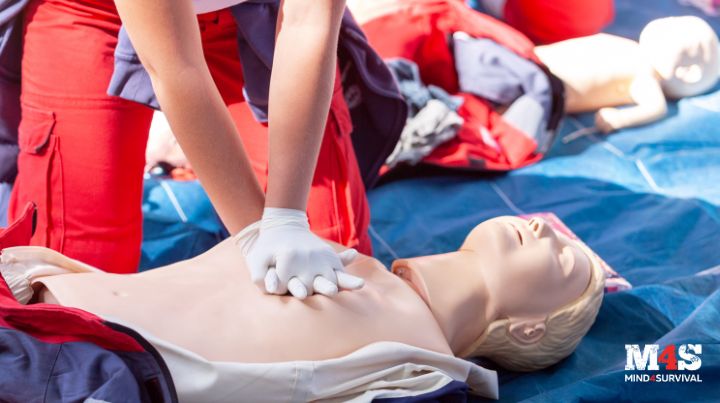
Preparedness isn’t just about stockpiling supplies. It’s also about equipping yourself with the knowledge and skills to use your supplies effectively. Basic first aid is essential for anyone serious about being prepared. In this article, I’ll cover fundamental first-aid skills everyone should know. As an experienced paramedic, I’ve seen firsthand how these skills can save lives.
Quick Look at What You’ll Learn
1. Stop the Bleed
Uncontrolled bleeding is a leading cause of preventable death and can kill a person within a few minutes. “Stop the Bleed” training teaches you how to control severe bleeding using direct pressure, pressure dressings, elevation, pressure points, and tourniquets, which are all techniques that can help manage bleeding until advanced care is available. This skill is critical for making sure you and those you love are kept safe and alive in disasters, car accidents, and other physical trauma-inducing emergencies.
Click here for Stop the Bleed training
2. C.P.R. (Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation)
C.P.R. is crucial for maintaining blood flow to the brain and heart in cases of cardiac arrest. When the heart stops beating or a person is unable to breathe, a lack of oxygen to the brain can cause irreversible brain damage and death in minutes. Most C.P.R. courses include instruction in the application of:
- C.P.R.
- Rescue breathing
- AED (Automated External Defibrillator)
- Choking management
Intervention with this training can double or even triple a person’s chances of survival. Knowing how to perform C.P.R. properly is a cornerstone of emergency preparedness. Moreover, once learned, it’s a life-saving skill people can use for the rest of their lives. There is no minimum age for C.P.R. training, so get certified as soon as you and your children can.
Here’s a link for the American Heart Association C.P.R. Training
3. Wound Care and Dressing
Disasters tend to be dirty, increasing the likelihood that wounds will get infected—turning minor problems into potentially serious ones. Understanding how to clean and dress wounds can prevent infections. Proper wound care involves cleaning the wound, applying an appropriate dressing, and knowing when to seek further medical help. This skill is critical for minor injuries and more complex situations, especially during disasters.
This is a link to First Aid Training with the Red Cross
4. Recognizing and Treating Shock
Shock can result from severe blood loss, infections, or traumatic injuries. Recognizing the signs—such as pale skin, rapid pulse, cool clammy skin, and altered mental state—and knowing how to respond can save lives. Treatment involves laying the person down, elevating their legs, and keeping them warm until help arrives.
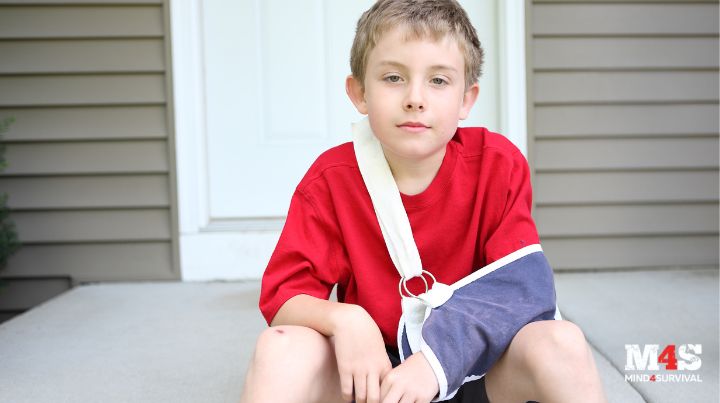
5. Splinting Fractures
Accidents and disasters result in falling objects, unstable ground, and impacts on the human body. One byproduct of those circumstances is broken bones. Fractures require the bones to be stabilized to prevent them from moving and causing further injury. Using available materials to apply a splint can help immobilize the injury and reduce pain.
6. Treating Burns
Fires are commonplace during disasters. As such, preparedness-minded people should learn how to treat burns ranging from minor to life-threatening. First-degree burns might only require cool water, while more severe second and third-degree burns need immediate professional care. Understanding the different types of burns and appropriate treatments is crucial to managing these painful and dangerous wounds.
7. Treating Hypothermia and Hyperthermia
Extreme temperatures can be dangerous. Hypothermia, or dangerously low body temperature, requires gradual warming and protection from further heat loss. On the other end of the thermometer, hyperthermia, or heat-related illness, requires cooling and hydration. Recognizing the symptoms and knowing the appropriate first aid measures for each are vital.
8. Recognizing and Managing Allergic Reactions
Allergic reactions can escalate quickly. It is crucial to know how to identify symptoms like swelling, hives, and difficulty breathing. In severe cases, using an epinephrine auto-injector (EpiPen) or other effective medications can be life-saving.
9. Identifying and Responding to Heart Attacks
Heart attacks require immediate attention. Symptoms can include chest pain, shortness of breath, and nausea. Acting quickly by calling emergency services and providing aspirin, if appropriate, can significantly improve outcomes.
10. Providing Care for Sprains and Strains
Minor injuries like sprains and strains are common. The R.I.C.E. method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation) helps reduce swelling and pain. Knowing this treatment technique can aid in recovery and prevent further injury.
11. Treating Poisoning and Overdoses
Accidental poisonings and drug overdoses require immediate action. Identifying the signs and knowing how to respond, such as by calling poison control or administering naloxone in the case of opioid overdoses, can be life-saving.
The Bottom Line on Basic First Aid Skills for Preparedness
Being prepared means more than having supplies in the back of a closet. It’s about acquiring the skills to respond to emergencies and effectively use your supplies and knowledge. These basic first-aid skills are foundational for anyone serious about preparedness and being able to take care of their loved ones. As someone who has dedicated their life to emergency response, I can’t stress enough the importance of being equipped with these abilities. Start learning these skills today and be your own first responder tomorrow.
Stay safe,

Read the full article here









